Advances in imaging for the assessment of calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease
Beyond Rheumatology 2022;
4
(3)
: e447
DOI: 10.53238/br_202212_447
Abstract
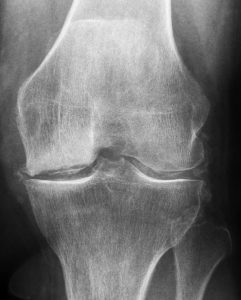
Calcium pyrophosphate (CPP) deposition (CPPD) disease is a common form of inflammatory arthritis. Despite its prevalence, it’s an under-studied condition and its diagnosis is still challenging. Even if the gold standard for the identification of CPP crystals is still synovial fluid analysis, several different imaging modalities were evaluated and were increasingly used to avoid invasive procedures. Conventional radiography is still considered the first-line radiological investigation thanks to its widespread availability and the long tradition in CPPD disease. However, in the last years major imaging advances have occurred with ultrasound (US) and dual-energy computed tomography (DECT): US has travelled the furthest and is the only validated imaging technique in CPPD; while DECT is the most promising tool for CPPD identification thanks to its capability to discriminate CPP crystals from other calcific deposits. CT is frequently used in case of axial involvement of the disease, and the role of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in CPPD has only been marginally studied. All these imaging techniques could support progress in CPPD diagnosis and management, as well as provide a deeper insight into the pathogenesis, clinical manifestation, and the natural history of the disease. The purpose of this review is to highlight the current knowledge and the recent advances on the most used imaging modalities, and their promising value in diagnosing CPPD.
To cite this article
Advances in imaging for the assessment of calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease
Beyond Rheumatology 2022;
4
(3)
: e447
DOI: 10.53238/br_202212_447
Publication History
Submission date: 10 Nov 2022
Revised on: 02 Dec 2022
Accepted on: 15 Dec 2022
Published online: 21 Dec 2022

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.